With our expertise in the manufacturing of plant-based medicines, we are committed to unlocking the significant therapeutic potential of this medicinal plant to benefit patients around the world

Patients in focus
Patients do not suffer from their illnesses alone but also from the symptoms and the burdens that come from coping with serious illness. The goal of our research is to develop cannabis-based products that have proven effective in relieving symptoms and improving quality of life.
We seek to bring relief to seriously ill patients.
This is why we are continuously developing and improving high quality cannabis extracts and APIs.
- With a standardized, predictable and consistent effects batch for batch
- Which fulfill all EU regulatory specifications and quality standards
- In a state-of-the-art pharmaceutical production facility that is Made in Germany
We cannot add days to a life but we can add life to days
Dame Cicely Saunders
ENDOCaNNaBINOID SYSTEM
The Endocannabinoid System (ECS) was first identified in the 1990s and is far from being fully understood by modern medical science. As the name suggests, the endocannabinoid system is endogenous to the human body and is present in some form in all organs and tissues. It is comprised of cannabinoid receptors, endogenous cannabinoids and enzymes that both synthesise and degrade these cannabinoids.1
1 Müller-Vahl KR, GrotenhernenF. Cannabis und Cannabinoide in der Medizin. MWV 2020; Hinz B. Pharmakon 2017; 2:109-117; Hoch E et al. Cannabis-Eine wissenschaftliche Bestandsaufnahme. Springer Verlag 2019
MEDICAL CANNABIS ACCESS
The cannabis plant has traditionally been used for therapeutic purposes for many hundreds, if not thousands, of years. In recent years, more and more patients and doctors have renewed interest in medical cannabis therapies. Countries around the world are granting patients access to medical cannabis albeit with very different rules and regulations. National healthcare authorities can inform patients and doctors about the status of access to these therapies in individual countries.
_ Medical Cannabis

Medical Cannabis products are understood to be magistral and officinal preparations from the cannabis plant. In the European Union they are produced in accordance with EU pharmaceutical regulations and standards for herbal drugs.1 These include different cannabis extracts as well as dried cannabis flowers.2
_ Cannabinoids
Cannabidoids found in the cannabis plant (phytocannabinoids) are a heterogeneous group of substances. These include neutral and (Carboxl-) acid containing substances.1 Over 100 cannabinoids have been isolated and a subsection of these have been found to have pharmacological effects on humans.
The most studied phyto-cannabinoids to date are Delta-9- Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC, Dronabinol) and Cannabidiol (CBD)
_ THC
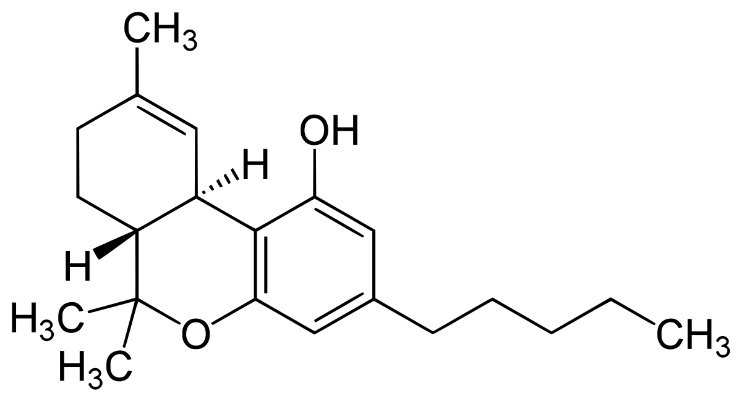
THC is the substance within the cannabis plant with a psychoactive effect. In the human body, THC interacts and binds with the receptors in the endocannabinoid system.
Clinical studies have demonstrated that THC can be effective in treating pain, anxiety, muscle spasms and nausea. Based on this body of empirical evidence, international medical and research experts have derived recommendations for the use of THC in the treatment of a number of illnesses including neuropathic and other forms of pain3 as well as for chemotherapy induced nausea and vomiting, spasticity in conjunction with multiple sclerosis, appetite stimulation and wasting in conjunction with HIV AIDS.4.
_ CBD
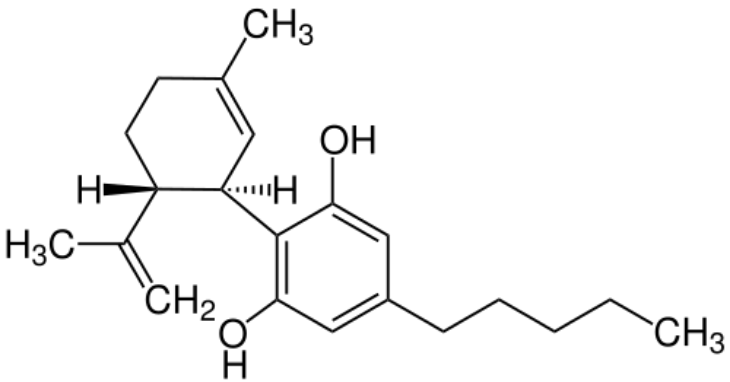
In addition to THC, CBD is the second cannabinoid to have demonstrated a therapeutic effect in clinical studies. In contrast to THC, CBD does not cause a psychoactive effect and binds with low affinity to the endocannabinoids receptors in the human body. CBD is able to modulate the effectiveness of the binding partner in the cannabinoid receptors. When taken in combination with THC, CBD can therefore counteract the psychoactive effect of THC.
CBD has also been shown to have anti-convulsive and anti-inflammatory properties. It is therefore used to treat refractory forms of epilepsy.
1. European Medicines Agency. Compilation of terms and definitions for Cannabis-derived medicinal products. vol. 31 (2021).
2. Veit, M. Quality Requirements for Medicinal Cannabis and Respective Products in the European Union – Status Quo. Planta Med. (2022) doi:10.1055/a-1808-9708.
3. Häuser, W. et al. European Pain Federation (EFIC) position paper on appropriate use of cannabis-based medicines and medical cannabis for chronic pain management. European Journal of Pain (United Kingdom) vol. 22 1547–1564 (2018).
4. National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. 2017. The Health Effects of Cannabis and Cannabinoids: The Current State of Evidence and Recommendations for Research. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press. https://doi.org/10.17226/24625.